Introduction
The Himalayan region is home to several fragile ecosystems that provide water, food, and livelihoods to millions of people. However, it is also one of the most disaster-prone regions in the world, with frequent earthquakes, landslides, and floods. The construction of large hydroelectric dams in the region has added another layer of risk, putting millions of people at risk of disaster. In this article, we will explore the dangers of Himalayan dams and the need to rethink their construction.

The Dangers of Himalayan Dams
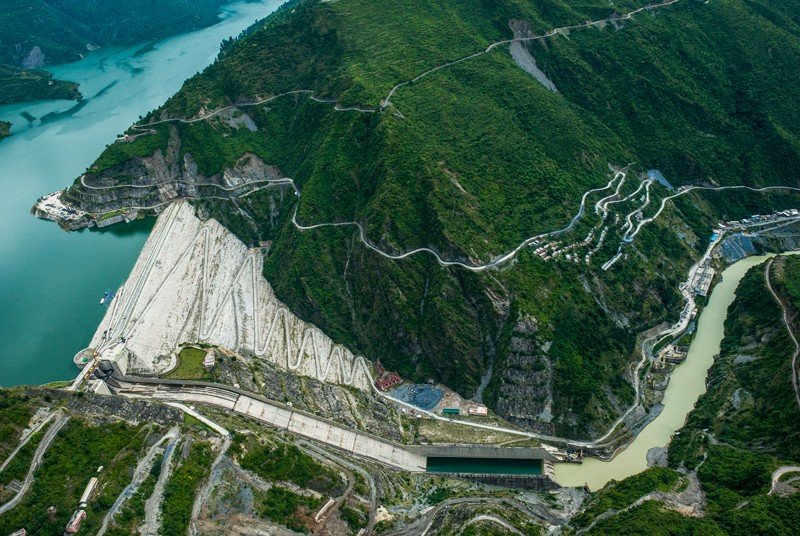
Dam construction in the Himalayan region poses a serious threat to the environment and people. The region is very active from a seismic point of view, with frequent earthquakes and landslides. Large dams built on unstable subsoil are very vulnerable to damage from such events, which can lead to catastrophic failures.
For example, the 2008 Sichuan earthquake in China caused several dams to collapse, killing thousands of people. Similarly, during the 2013 Uttarakhand floods, several hydroelectric dams in the region were inundated, causing massive flooding that caused major damage and loss of life.

Examples of Himalayan Dams
The Tehri Dam is one of the largest dams in India and was built on the Bhagirathi River in the state of Uttarakhand in the late1990s. The dam is designed to generate hydroelectric power and provide water for irrigation and drinking. However, the construction of the dam had significant environmental and social impacts. The dam has displaced more than 100,000 people, who have been forced to flee their ancestral lands.
The dam also caused significant environmental damage, resulting in the flooding of large areas of forest and the loss of valuable ecosystems. The construction of the dam on highly seismically active land has raised concerns about its safety and the potential for catastrophic failure in the event of a major earthquake.
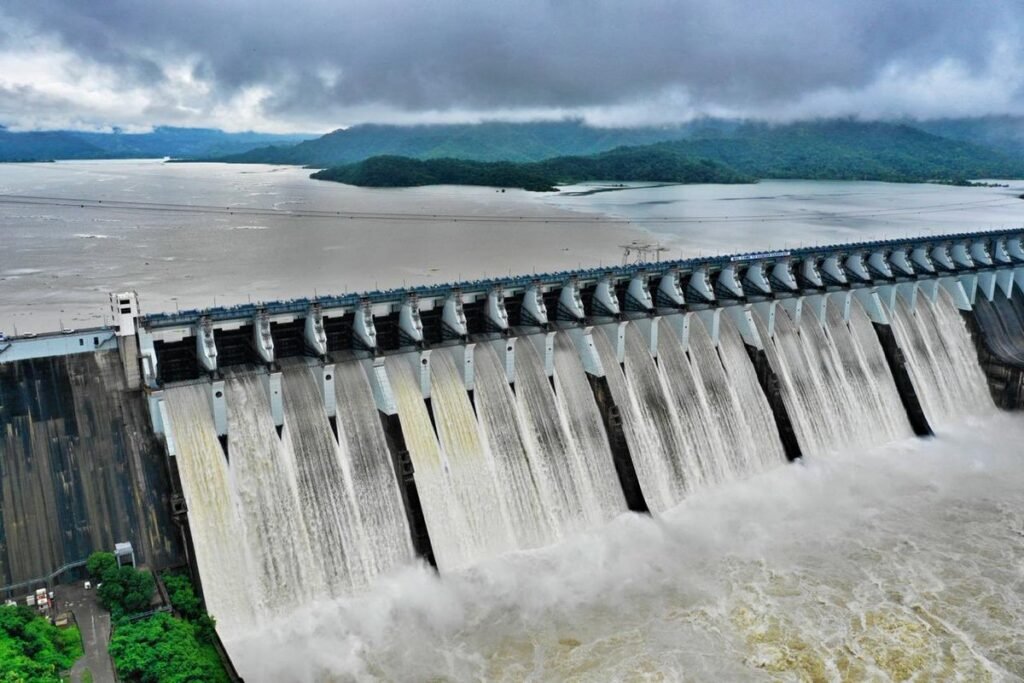
The Sardar Sarovar Dam, located on the Narmada River in Gujarat, is another example of a large dam in the Himalayan region that has faced significant controversy. The dam was constructed to provide water for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation but has been criticized for its impacts on local communities and the environment. The construction of the dam has led to the displacement of thousands of people who have lost their homes, lands, and livelihoods.
The dam has also caused significant environmental damage, including flooding of forests and other ecosystems, loss of biodiversity, and disruption of natural river systems. In addition to these concerns, questions have also been raised about the safety of the dam and the adequacy of its design and construction.

Environmental Impact of Himalayan Dams
The construction of large hydroelectric dams in the Himalayan region can have devastating effects on the environment the natural course of rivers, disrupting ecosystems, and leading to a loss of biodiversity. These impacts include habitat destruction, water quality degradation, sediment accumulation, climate change, seismic hazards, and deforestation. When dams are built, they can flood large areas of land, destroying plant and animal habitats and altering water quality. In addition, dam construction contributes to climate change and may pose significant risks due to seismic activity.
Deforestation is also a serious problem, with forested areas often being cleared for the construction of dams to ensure sustainable development and protect the natural resources of the Himalayan region, the environmental impact of future dam projects must be carefully assessed.
Rigorous environmental impact studies must be conducted to consider the long-term impacts of these projects on the environment and local communities. Alternative energy sources such as solar and wind power should also be considered to reduce reliance on hydropower and reduce the environmental impact of dam construction.
Conclusion
Dam construction in the Himalayas is a recipe for disaster, exposing millions of people to catastrophic events. The risks associated with building large dams in the region are significant, as are the environmental and social consequences associated with building large dams in the region are significant, as are the environmental and social consequences. The need for sustainable development in the region is urgent, and alternative solutions must be explored to meet the region’s energy and water needs. International agreements and funding organizations can play a key role in promoting sustainable development in the region.
However, achieving sustainable development requires a shift in priorities and a willingness to prioritize environmental and social well-being over short-term economic gains. Only in this way can the Himalayan region develop sustainably and protect its fragile ecosystems and communities.

Where Luxury Meets Bali: A Guide to the Island’s Top 6 Most Expensive Hotels Trybe News