Introduction
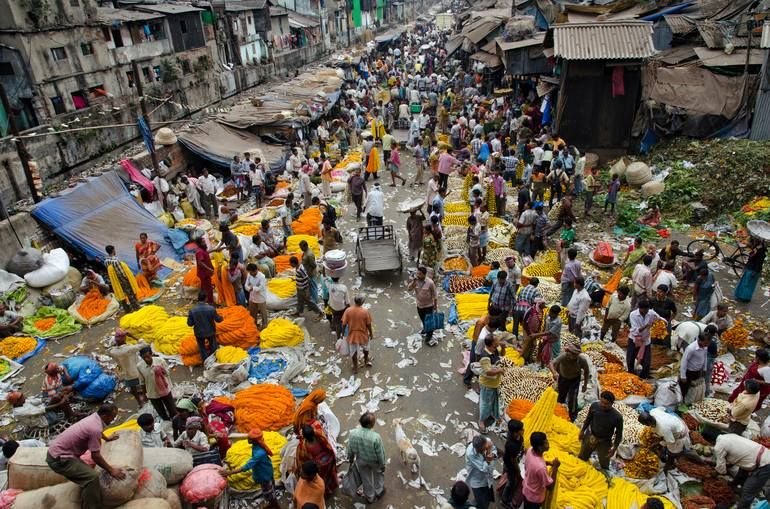
India, known for its vibrant culture, diverse traditions, and bustling cities, has also earned another distinction: being the world’s second-most populous country. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India faces a unique set of challenges due to its population explosion.
India’s population explosion can be attributed to various factors, including cultural, social, and economic influences. One of the contributing factors is the traditional preference for large families. The notion of “hum do, humare do” humorously captures the Indian mindset favoring bigger families. The desire for a male child, combined with societal expectations and economic reasons, has led to larger family sizes in many parts of the country.

Fear of Overpopulation
The fear of overpopulation in India stems from the significant challenges posed by managing such a massive population. With limited resources and inadequate infrastructure, sustaining and providing for a growing population becomes increasingly difficult. The strain on natural resources, such as water, land, and energy, becomes more pronounced as the population expands.
As the population increases, so does the demand for essential resources like food, water, housing, and healthcare. The growing demand puts a tremendous strain on the availability and equitable distribution of these resources. Inadequate access to these essentials leads to shortages, disparities, and further socio-economic imbalances.
A high population often leads to increased unemployment rates and poverty levels. The economy struggles to create sufficient job opportunities to absorb the growing workforce. This imbalance results in economic instability and social unrest, hindering progress and development.
A large population also contributes to environmental degradation. Rapid urbanization, deforestation, increased pollution, and higher carbon emissions strain the delicate ecological balance. The pressure on natural resources intensifies, leading to overexploitation and degradation of ecosystems. Overpopulation also poses challenges in waste management and maintaining a sustainable environment.
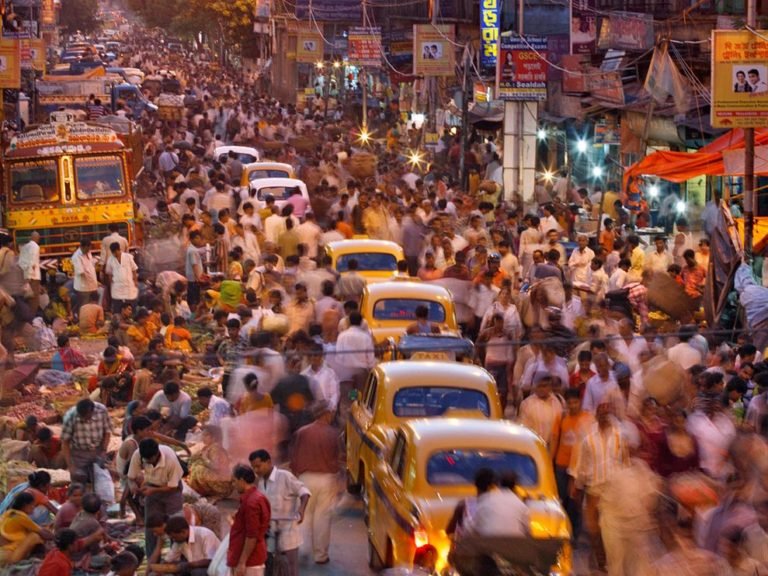

The Downside of Over Population
The increasing demand for resources surpasses the available supply. This results in food scarcity, water shortages, housing crises, and inadequate access to healthcare and education. The lack of equitable distribution exacerbates socio-economic disparities within the population.
With a large population competing for limited job opportunities, unemployment rates rise. This, in turn, leads to widespread poverty and income inequality. Insufficient employment opportunities hinder economic growth and social progress.
Overpopulation puts immense pressure on existing infrastructure, leading to substandard living conditions. Inadequate housing, congested roads, insufficient public transportation, and overwhelmed healthcare systems are some of the consequences. As a result, the quality of life for many citizens suffers, and access to essential services becomes challenging.

Highest Fertility Rate
India has made progress in reducing its fertility rate, but it remains relatively high compared to many other countries. Several factors contribute to this trend, including cultural and social norms, limited awareness and access to contraception, and a preference for larger families.
To address the population bubble effectively, there is a need to focus on comprehensive family planning initiatives. This involves promoting awareness about the benefits of smaller families, providing accessible and affordable contraception methods, and empowering women with education and reproductive rights. Comprehensive sex education plays a vital role in educating the population about reproductive health and responsible family planning choices.
By prioritizing effective family planning measures, India can control population growth, alleviate the strain on resources, reduce unemployment rates, and improve the overall well-being of its citizens.
Conclusion
India’s population bubble, reflected humorously in the slogan “hum do, humare do,” presents a complex challenge for the country. While the cultural, social, and economic factors contributing to high population are deeply ingrained, the fear of overpopulation and its detrimental consequences cannot be ignored.
India must prioritize effective family planning, sustainable resource management, and equitable development to address the downsides of overpopulation and ensure a brighter future for all its citizens. Through concerted efforts, India can find a balance where “hum do” (we two) coexists harmoniously with a more sustainable population size.




